When excessive background noise and reverberation are not addressed, it can make it hard to hear and understand speech. This is especially important for younger students where excessive noise may lead to students missing key words, phrases and concepts.
Good acoustic design will support students with hearing impairment and those with learning difficulties, while poor acoustics can be especially hard for students where English is not their first language.
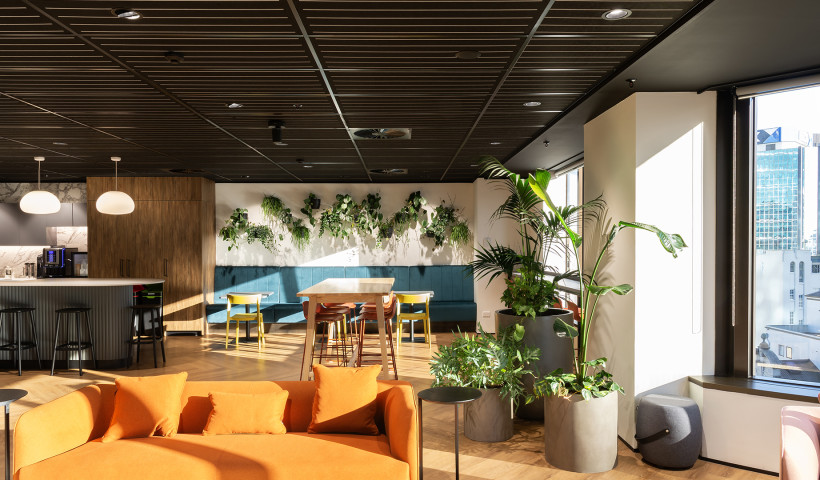
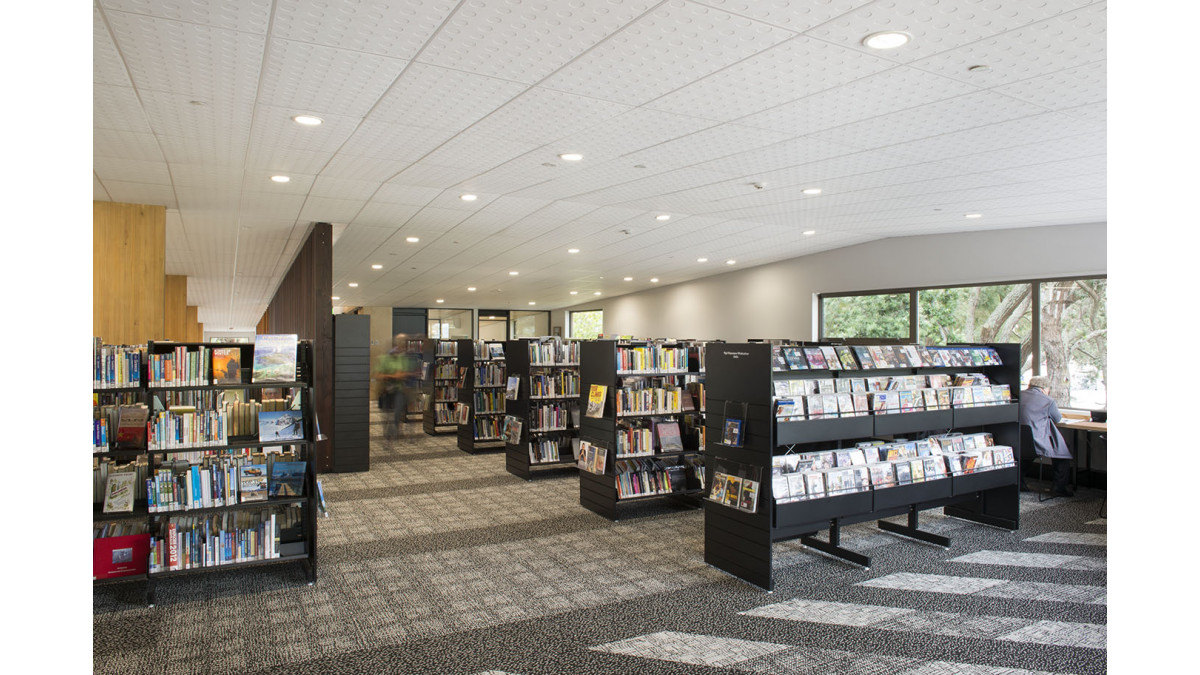
Many schools are choosing to create flexible learning spaces. These can provide significant benefits by connecting a larger number of students in parallel activities that support the diverse learning needs of students. However, just as in traditional classrooms, it is important that these flexible spaces are acoustically engineered to address potential background noise.
The Oticon Foundation study in NZ primary school classrooms noted that:
- 71% of teachers felt that internal classroom noise was a problem
- More than 33% of teachers indicated they had to speak at a level that strained their voices
- Around 50% of teachers said they had to considerably raise their voices during group work
For those currently working on refurbishing or designing a new school building, the new mandatory changes to the DQLS (Designing Quality Learning Spaces) document will help overcome these acoustic issues.
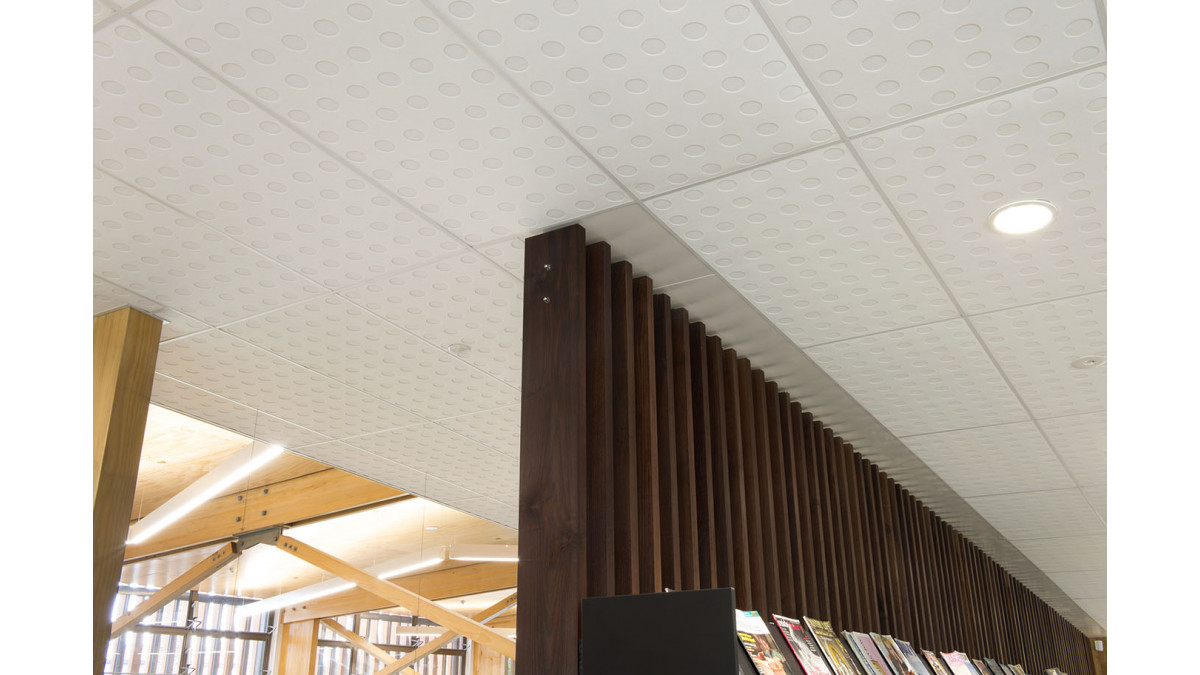
One of the most important changes for new and refurbishing school projects is that learning spaces must have a full ceiling coverage made with a high performance absorptive product with a minimum NRC of 0.85 in addition to a wall treatment.
Asona's glass fibre Triton Range of ceiling panels comes in a variety of thicknesses from 15 — 100mm and starts at NRC 0.85 up to 1.00. Made from high density glass fibre faced with a propriety glass mat composite facing, the panels are Group 1 fire rated, Global GreenTag certified and come in standard and custom-made sizes all the way up to 1200 x 3000mm.
The DQLS document also recommends that an absorptive acoustic wall treatment, such as glass fibre or pinboard panels, is used on all available walls, equivalent to at least 20% of the ceiling area and as thick as practicable — ideally 50mm or more with a noise coefficient of 0.85 to control the low frequency performance of the entire learning space.
Asona's Triton Fabwall was developed for just such a purpose and comes in thicknesses ranging from 50–150mm. Made from high density glass fibre faced in 2ply glass matt composite, then wrapped in fabric, these standard or custom-made panels have an NRC 1.00 rating and are Global GreenTag certified.
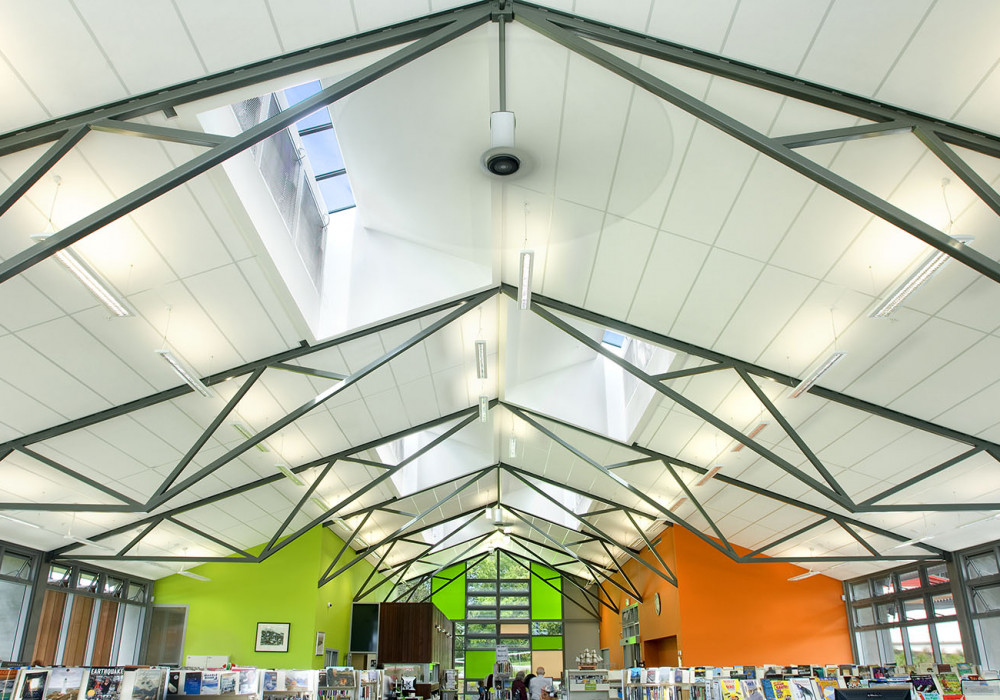
Noise from outside was another issue highlighted in the DQLS. Flexible learning spaces are typically large open spaces with large roof areas and the control of rain noise needs to be considered. Designers are now required to achieve a roof and ceiling sound performance of NC 45 or less.
Asona's Triton Duo 60 was created to control rain attenuation, made as a 60mm thick dual layer composite class A absorber and attenuator ceiling panel with Sonatex facer on a 50mm absorber combined with a high mass 740 kg/m³ 10mm attenuator backer. It is designed for maximum sound absorption and attenuation of transmitted rain noise under metal roofing.
The latest DQLS Acoustic Version 2.0 is mandatory for all projects starting after 1 January 2017.











 New Products
New Products























 Popular Products from Asona
Popular Products from Asona


 Most Popular
Most Popular


 Popular Blog Posts
Popular Blog Posts
