
There are a number of approaches that can be used to show compliance with H1 clause, it's complicated and it is up to the designer to create a house that meets the new building envelope R-value. Pink Batts has developed the accompanying technical update to help designers to understand the effect of the changes to H1, outlining methods of complying with H1.
Introduction
The main objective of clause H1 in the New Zealand building code is to facilitate efficient use of energy. It applies to all residential dwellings and all other buildings less than 300m2.
The change in the code now sees us building more sustainable homes with higher levels of insulation than we have ever had. This higher level of insulation reduces energy lost, when heating and cooling buildings.
Compliance
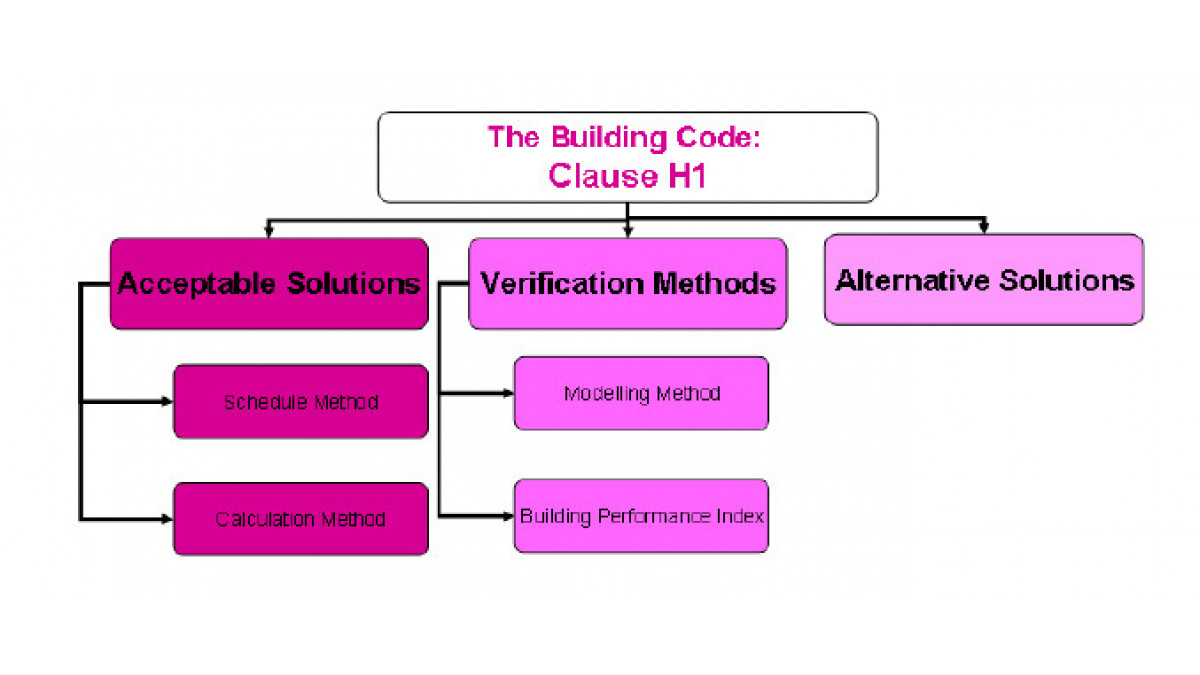
There are several methods with which compliance can be met as show below:
Using an Acceptable Solution will automatically comply with the building code.
The Verification method will provide a means of that a building complies with the Building Code.
Alternative solution is just that, allowing designer to come up with an alternative solution.
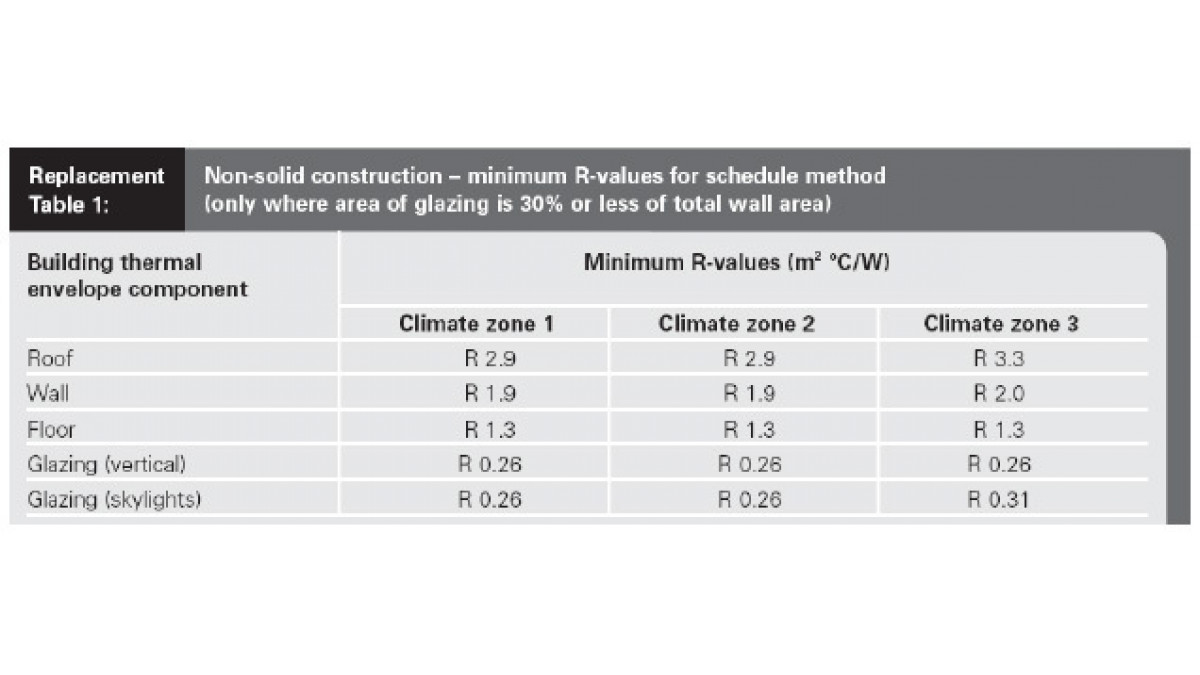
Acceptable Solution: Schedule Method
Meet minimum construction values taking into account:
- Climate zone
- Construction Method
- Insulation material R-value
- Thermal bridging.
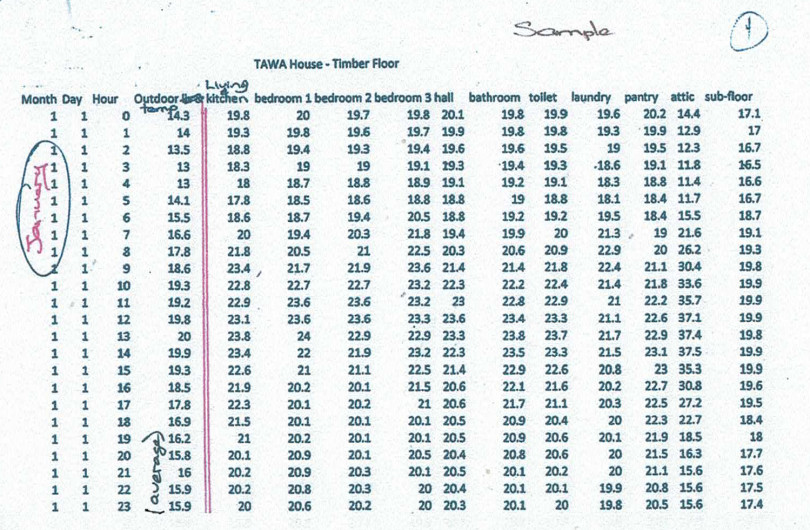
Table1 from H1 is shown above. You can download the clause including all the tables and associated notes via the Department of Building and Housing website.
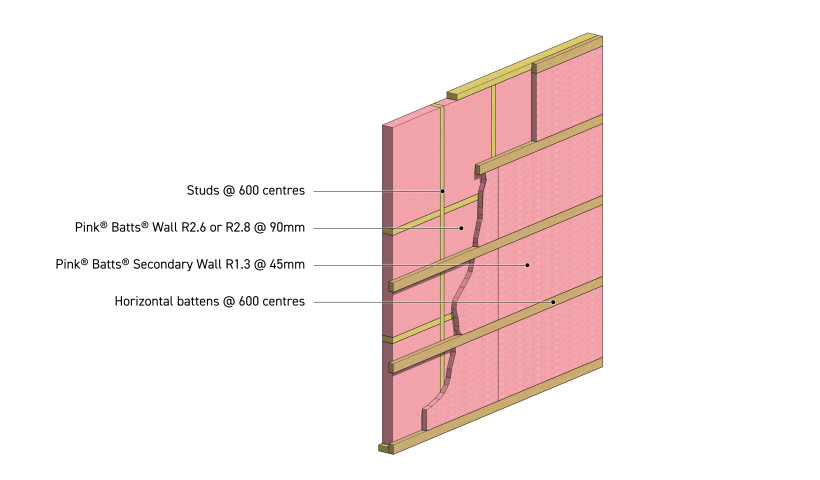
Another table above shows construction R-values required to be achieved to meet compliance. Construction R-values takes in account thermal bridging, cladding materials and other factors, and as shown below, the R-value of the insulation itself is not the same as the final construction R-value.
The Pink Batts R-value Insulation Guide provides the Insulation R-values required, achieving the Construction R-values necessary to comply with NZBC Clause H1.
Alternatively the BRANZ House Insulation Guide 3rd Edition provides the Insulation R-values required achieving the Construction R-values in greater detail.
Acceptable Solution: Calculation Method
The Calculation Method:
- Allows for buildings with mixed construction types
- Uses reference building to calculate minimum construction R-values.
The Heat Loss (HL) of the proposed building must be less than the HL of the reference building. Where A is the area of the building element and R is the Construction R-value.
Refer to NZS 4218:2009 Thermal Insulation - Housing and Small Buildings for further details and worked examples.
Verification Method: Modelling Method
- Use of software programme to model building, other factors such as environment
- Required for complicated designs and where glazing is > 50% of total wall area.
Complex Modelling Programmes such as SUNREL meet the modelling requirements as set out by NZS 4218.
Verification Method: Building Performance Index
- Use of Building Performance Index (BPI) as stated in H1
- Can use BRANZ ALF Method ( Annual Loss Factor) software programme to model the building.












 Case Studies
Case Studies













 Popular Products from Comfortech Building Performance Solutions
Popular Products from Comfortech Building Performance Solutions


 Posts by Comfortech Technical
Posts by Comfortech Technical Most Popular
Most Popular


